Are you struggling to attract organic traffic to your website?
Do you find yourself questioning whether Google has even indexed your site?
If you’re experiencing a lack of organic traffic, the reason may be a failure to index your site with Google.
When Google fails to index your site or a webpage, it essentially is invisible to audiences searching on the platform, resulting in a significant missed opportunity for traffic generation.
But fear not, as there are proven methods to help indexing and ensure your site appears in Google’s search results.
In this post, we’ll discuss the strategies to help you index your site on Google.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started.

Table Of Contents
- What is Google Indexing?
- How to Check if Google Has Indexed Your Site
- How to Index Your Site on Google
- Check WordPress Settings for Search Engine Visibility
- Submit Your Sitemap
- Use Instant Indexing
- Monitor Your Indexing Status
- Check robots.txt for Crawl Issues
- Make Sure There’s No Duplication of Pages
- Remove Unwanted Noindex Tags
- Check for Nofollow Internal Links
- Build Powerful Internal Links
- Build High-Quality Backlinks
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
1 What is Google Indexing?
Google indexing is the process by which Google’s search engine collects, analyzes, and stores information from web pages across the internet.
In simpler terms, it’s how Google keeps track of all the online content, organizing it in a massive database to retrieve and display it in search results when the audience performs relevant queries.
When a webpage is indexed by Google, it means that the content of that page has been evaluated and added to Google’s index, making it eligible to appear in search results. This process involves Google’s bots, also known as crawlers or spiders, visiting and analyzing the content of web pages, following links, and determining the relevance and quality of the information they find.
For example, consider our blog post about “Schema Markup”.
When Google’s bots crawl our website and index this specific blog post, it means that Google has stored information about the title, content, images, and other relevant details of our post in its index.
Now, when someone searches for “Schema Markup” on Google, our blog post appears in the search results as Google determines that it’s relevant and authoritative for that query.

2 How to Check if Google Has Indexed Your Site
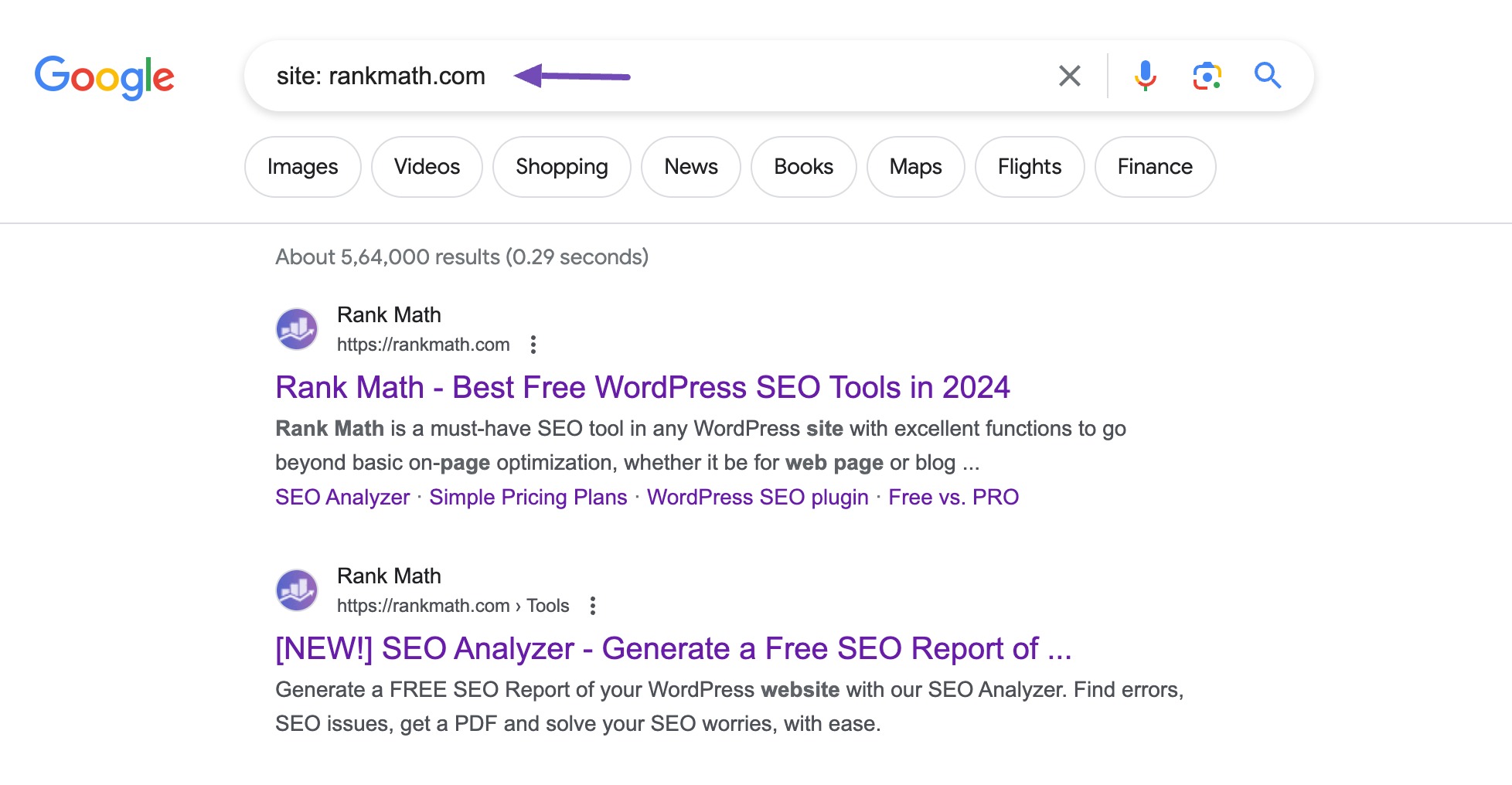
The simplest method is to perform a site-specific search on Google using search operators.
Type “site:yourwebsite.com” into the Google search bar, replacing “yourwebsite.com” with your domain name. This query will display all pages from your site that Google has indexed.
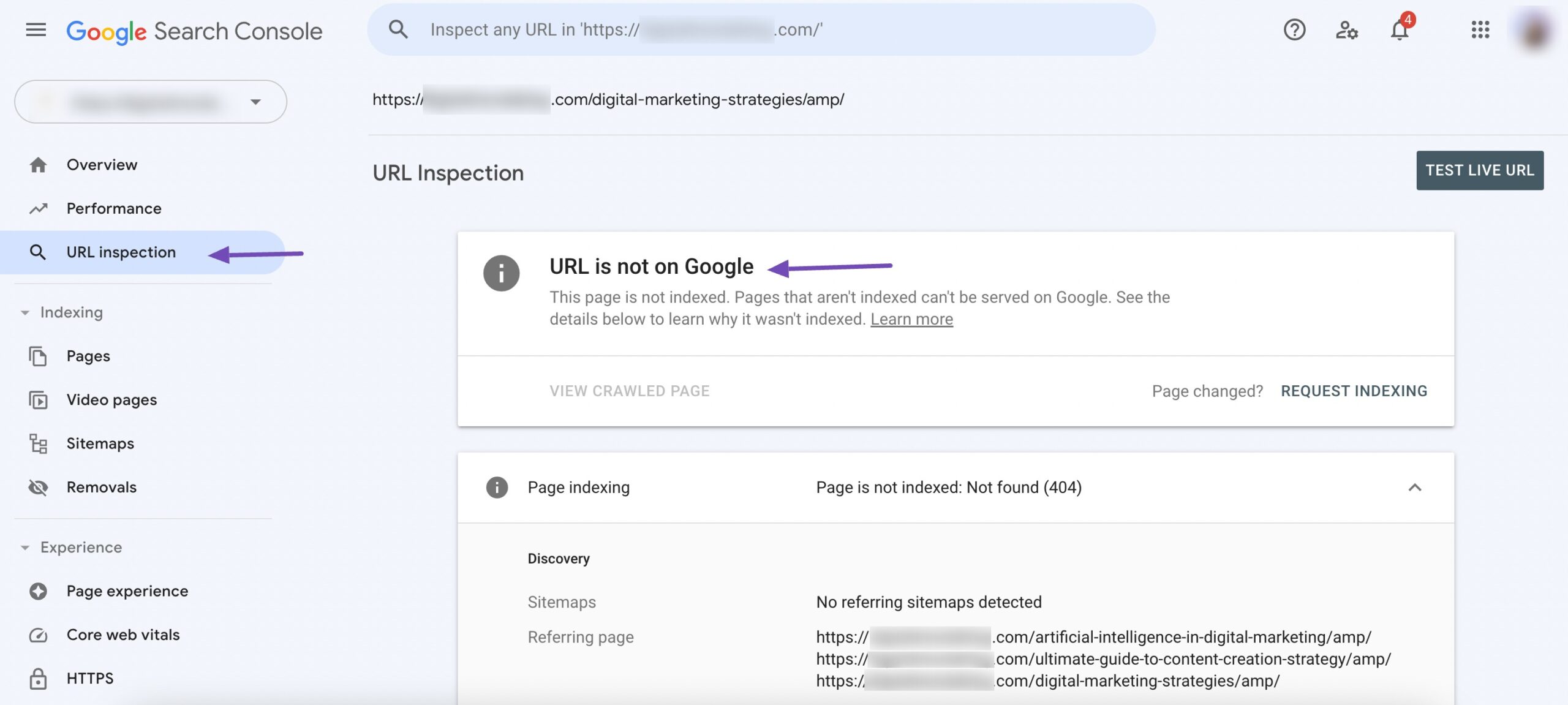
You can also use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console. Enter the page URL to check if it is indexed or not in the URL Inspection tool.
If the page is indexed, you’ll notice a message saying the URL is on Google, as shown below.

If the page is not indexed, the below message will be displayed in Google Search Console.
3 How to Index Your Site on Google
Let us now discuss the ways to index your site on Google.
3.1 Check WordPress Settings for Search Engine Visibility
Checking WordPress settings for search engine visibility helps ensure your website is accessible to search engines and can be properly indexed and ranked in search engine results pages (SERPs).
To access these settings, navigate to the WordPress admin dashboard and click on the Settings → Reading section.
Here, you’ll find the Search engine visibility section, which contains a checkbox labeled Discourage search engines from indexing this site, as shown below.
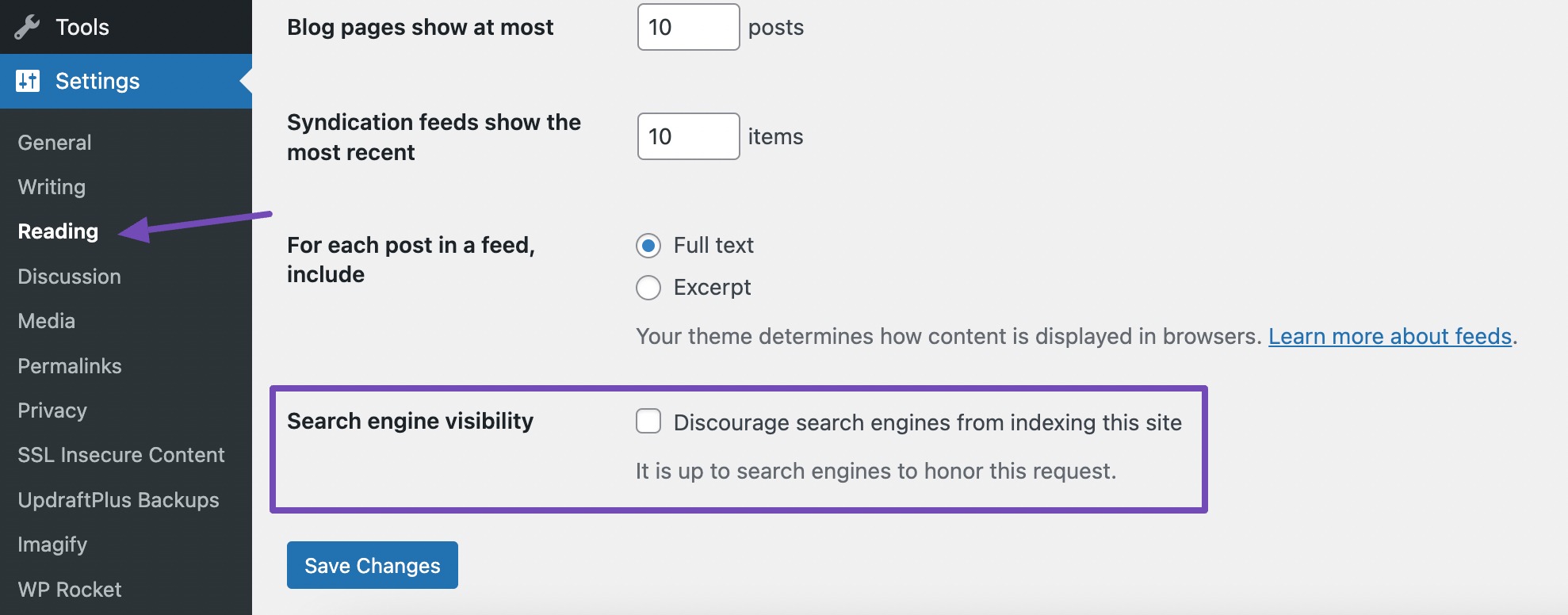
It’s important to ensure that this checkbox is unchecked. If checked, it will instruct search engines not to index your site, making it invisible to audiences in search engine results.
By unchecking this option and saving the changes, you confirm that your website is open to indexing, and search engines can index your site.
3.2 Submit Your Sitemap
By submitting an XML sitemap to search engines like Google through Google Search Console, you can ensure that all relevant pages are discovered and indexed efficiently.
Rank Math makes it very easy to submit your sitemap to Google. Install and activate the Rank Math plugin on your WordPress website if you haven’t already.
Upon activation, Rank Math will prompt you to configure its settings. Follow the setup wizard to input basic information about your website, such as its name, type, and preferred settings for SEO features.
Below are the sitemap settings that you can configure in the setup wizard.
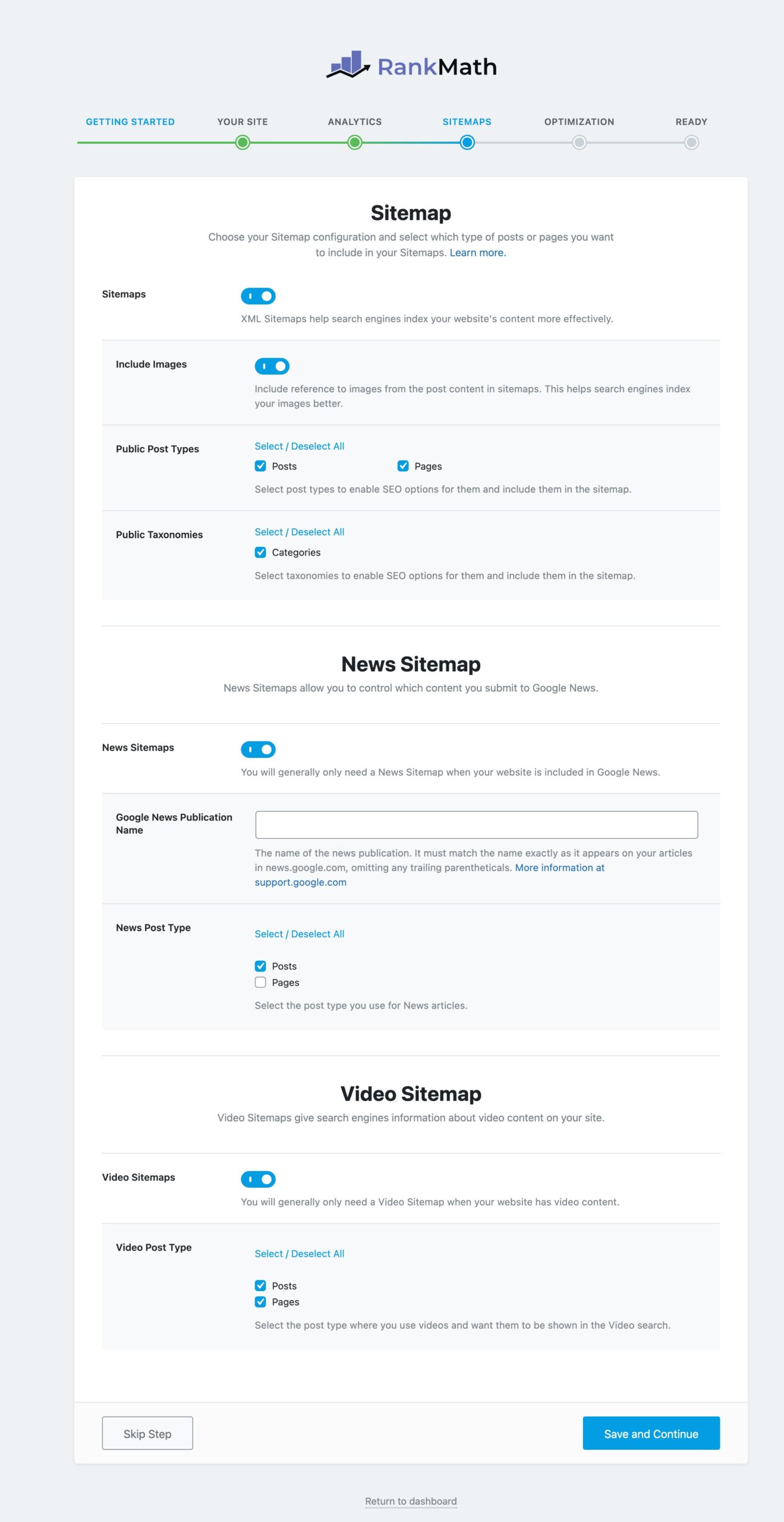
To locate your sitemap, navigate to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Rank Math SEO→ Sitemap Settings. Here, you’ll find the URL of your sitemap file.
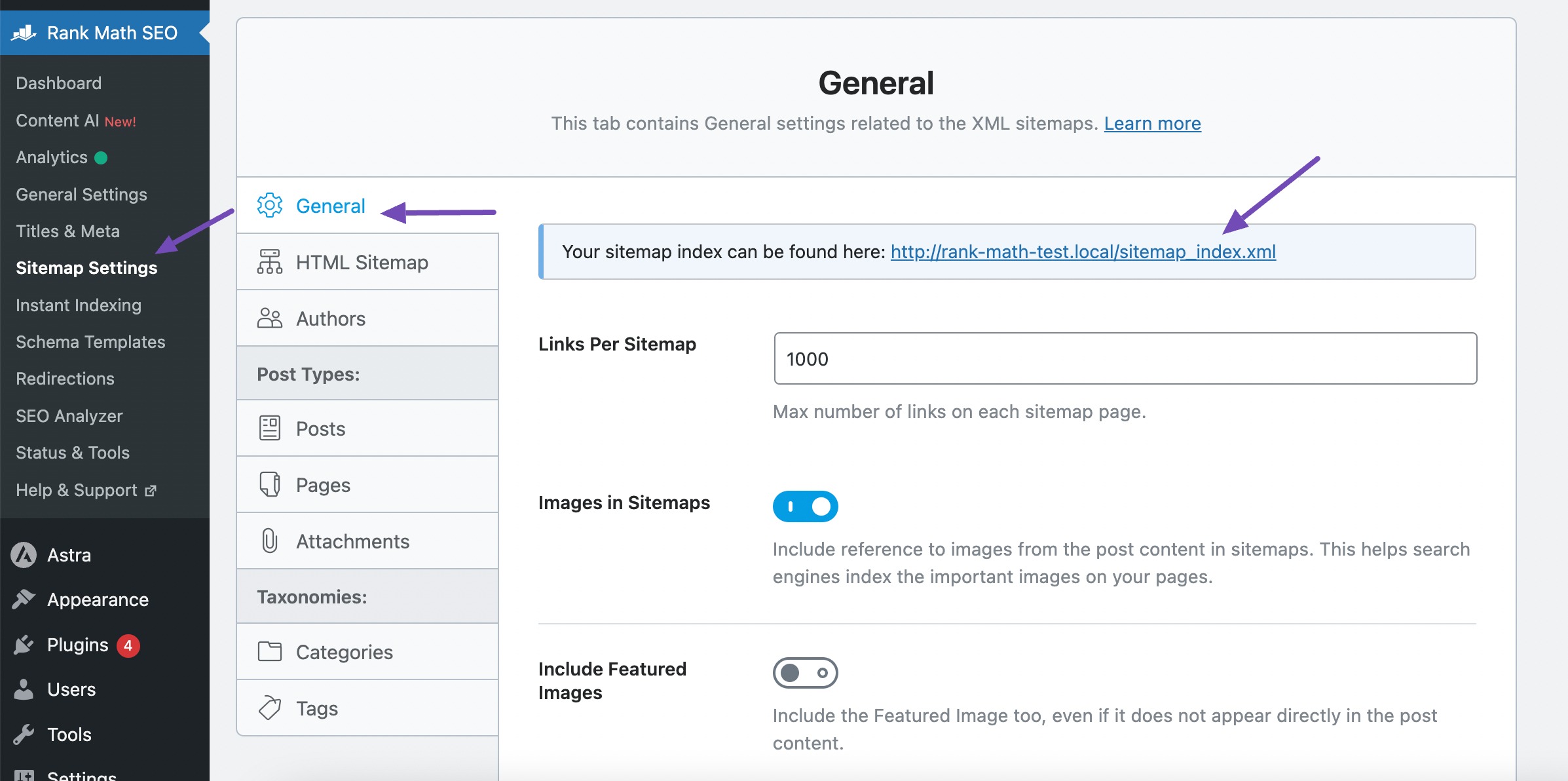
If you haven’t added your website to Google Search Console yet, you’ll need to do so first. Once logged in, select your website property from the list of properties.
In the left-hand menu, click Sitemaps under the Indexing section.
Enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://example.com/sitemap_index.xml) into the provided field and click SUBMIT.
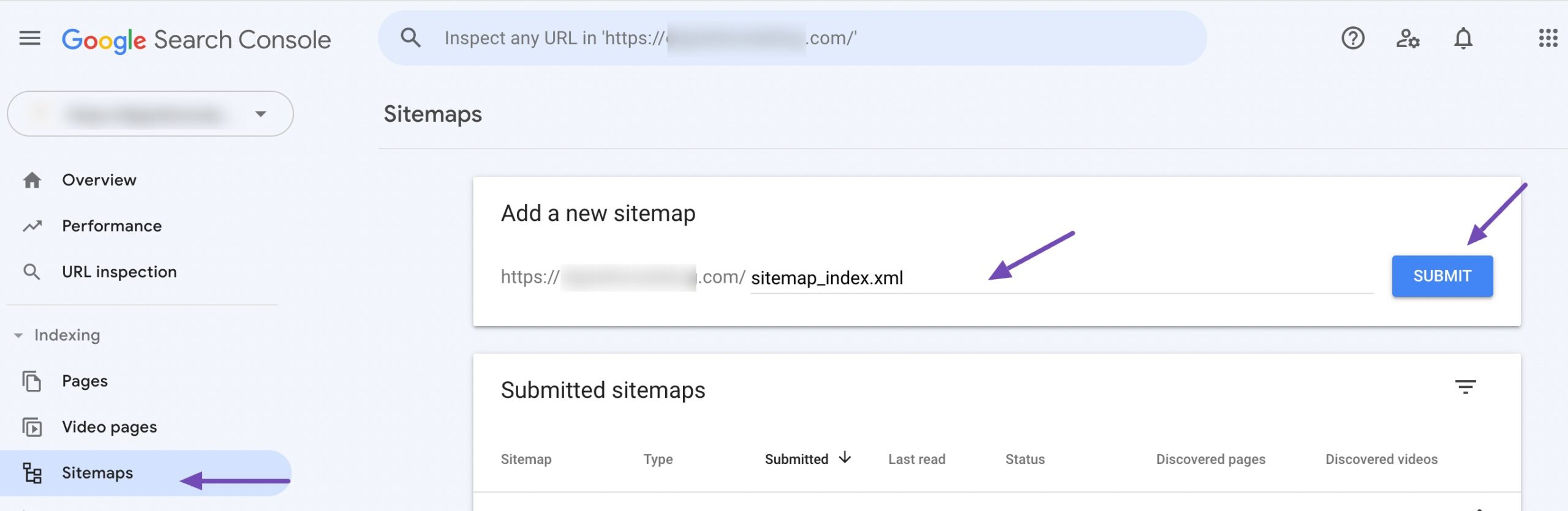
After submitting your sitemap, Google will display a message confirming the submission. It may take time for Google to process the sitemap and index your website’s pages.
Rank Math submits your sitemap index automatically to Google if you have connected Rank Math with your Google Search Console account. You can refer to its dedicated knowledgebase tutorial.
3.3 Use Instant Indexing
Instant Indexing in Rank Math helps index your site’s new content faster by search engines like Bing, Yandex, etc.
To use this feature, install and activate Instant Indexing for Google plugin on your site. Once done, navigate to Rank Math SEO → Instant Indexing → Console, add the URLs you want to index, and click the Send to API button, as shown below.
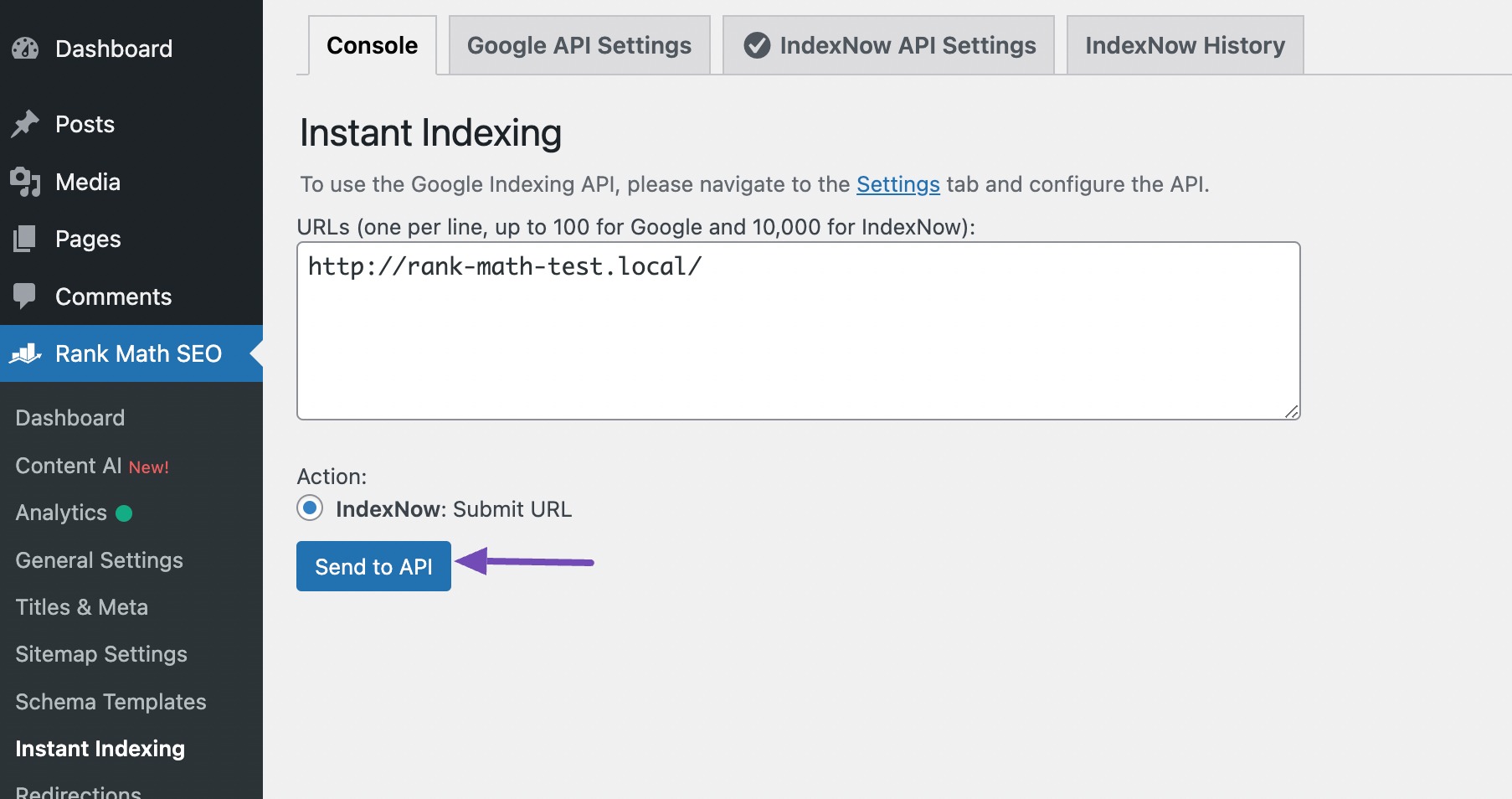
You can also use IndexNow to submit your URLs to the search engines instantly.
3.4 Monitor Your Indexing Status
You should track how search engines index your site, identify any errors or issues encountered during the process, and ensure your content is visible to your audience in search engine results.
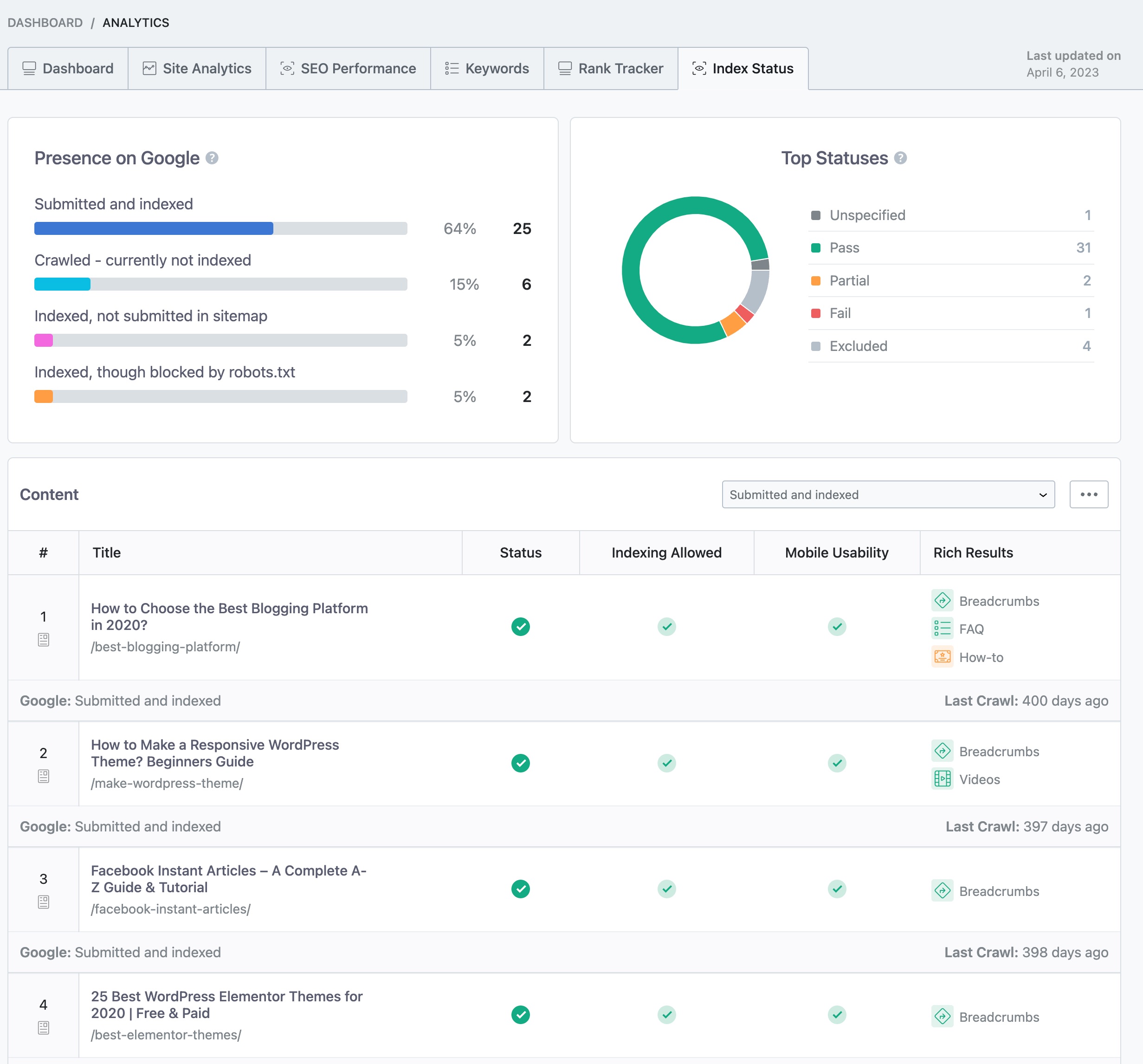
Rank Math’s Index Status allows you to monitor the indexing status of the website’s pages directly within the Rank Math plugin interface.
It provides valuable insights into how many of your website’s pages have been indexed by search engines like Google, helping you assess the effectiveness of your SEO efforts and identify any potential indexing issues that may need attention.
3.5 Check robots.txt for Crawl Issues
The robots.txt file serves as a set of instructions for search engine crawlers, specifying which pages or directories they should or should not crawl.
Identifying and resolving any issues within this file ensures that search engines can effectively navigate and index your website’s content.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on editing robots.txt file using Rank Math.
Once you’re in the robots.txt tab, review the file’s contents carefully to ensure that the directives accurately reflect your website’s intended crawling and indexing instructions.
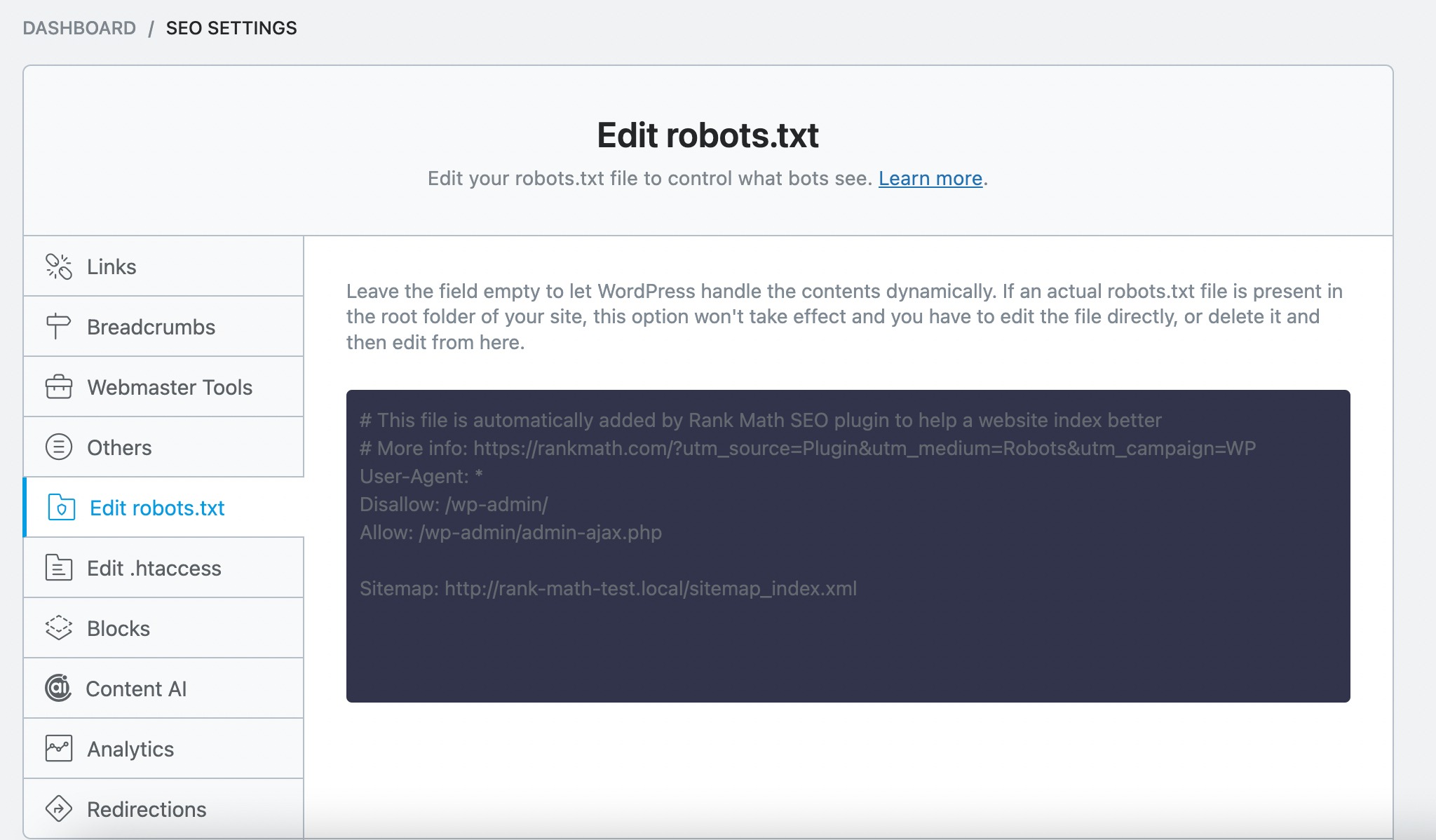
If you identify any crawl issues, such as blocking essential content or syntax errors, take immediate action to resolve them.
This may involve adjusting disallow rules, correcting syntax errors, or removing outdated directives. Once you’ve made the necessary modifications, save your changes within the Rank Math interface.
3.6 Make Sure There’s No Duplication of Pages
Duplicate content can confuse search engines, leading to indexing issues and potentially harming your website’s rankings.
If you have multiple pages that serve the same purpose or contain similar content, consider consolidating them into a single, comprehensive page and remove the rest using a 301 redirect to the main page. This can help eliminate duplicate content issues and streamline your website’s structure.
Implement canonical tags on duplicate pages to inform search engines which version should be indexed and ranked in search results.
3.7 Remove Unwanted Noindex Tags
Noindex tags instruct search engine crawlers not to index your site or specific web pages, effectively preventing them from appearing in search engine results pages (SERPs).
However, if these tags are applied incorrectly or inadvertently to essential pages, it can hinder your site’s visibility and indexing by search engines.
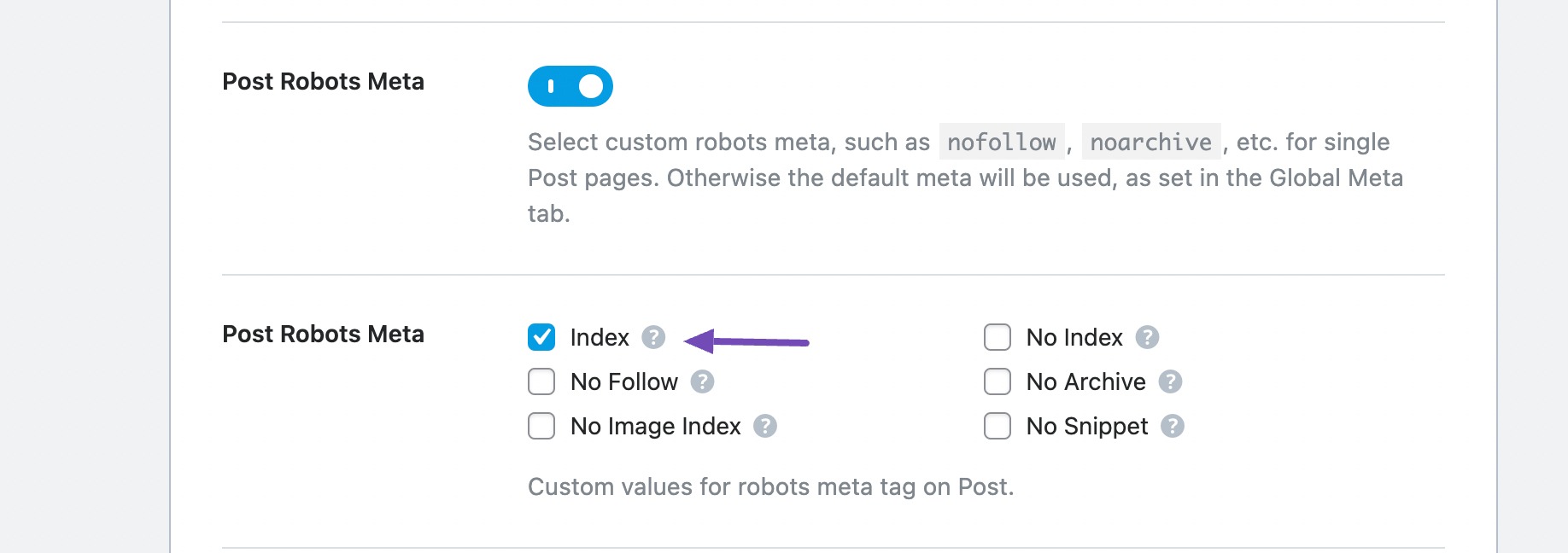
If you’re using Rank Math, navigate to Titles & Meta → Global Meta settings and ensure the Robots Meta is set to Index.

Similarly, check for the Post/Page Robots Meta.
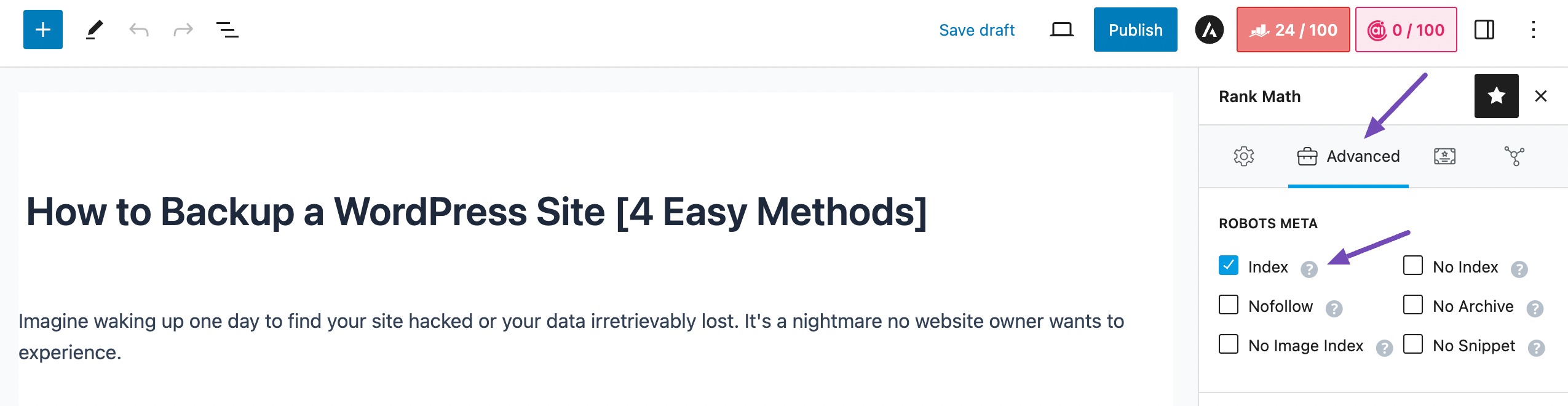
You can also check an individual page/post by navigating to the Advanced tab in the Rank Math SEO meta box. Ensure that the ROBOTS META is set to Index, as shown below.
3.8 Check for Nofollow Internal Links
A “nofollow” link is an HTML attribute that tells search engine crawlers not to follow the link to its destination.
While it’s common to use nofollow attributes for external links, applying them to internal links may inadvertently affect the indexing and ranking of important pages on your website.
You can verify nofollow links in the same manner as you check the noindex tag with Rank Math. Doing so will help Google index your site and ensure that your valuable content receives the visibility it deserves in search engine results pages.
3.9 Build Powerful Internal Links
Internal links are important in helping Google discover content on your website as it navigates from link to link.
However, if a page on your website lacks internal links, Google may struggle to explore other content on your site, which can delay indexing your site’s additional pages.
To solve this, consider including internal links strategically within your content to guide Google to relevant areas of your website.
But what exactly constitutes a powerful internal link?
For instance, if your website features pages that attract the most traffic and rank well on Google, offering valuable content to the audience. By internally linking from these high-traffic posts to other pages on your site, you establish robust internal links that enhance navigation and indexing efficiency.
You can track the internal links using Rank Math’s link counter.
3.10 Build High-Quality Backlinks
Backlinks, or inbound links, are links from external websites pointing to your site. Google views backlinks as votes of confidence, indicating that other websites consider your content valuable and authoritative.
Backlinks play a significant role in indexing by increasing your content’s discoverability.
When a reputable website with substantial traffic links to your site, search engine crawlers are inclined to follow these links. Consequently, this process facilitates the discovery of new pages and content on your website that require indexing.
Refer to our link-building tutorial and explore the simplest link-building methods.
4 Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it typically take for Google to index a new website?
Google’s indexing process varies, but new websites can be indexed within a few days to weeks.
Why is it essential to ensure crawlability for website indexing?
Ensuring crawlability means ensuring search engine bots can access and navigate your site easily. It’s important for indexing because if search engines can’t crawl your site, they can’t index its content.
Is it necessary to regularly update website content for indexing purposes?
Yes, regularly updating and refreshing content signals to search engines that your site is active and relevant, potentially leading to more frequent indexing and higher rankings.
What should I do if my website’s indexing suddenly drops?
If your website’s indexing drops suddenly, investigate potential issues such as crawl errors, duplicate content, or manual penalties. Addressing these issues promptly can help restore indexing and rankings.
5 Conclusion
Effectively indexing your site on Google is essential for improving its visibility and attracting organic traffic.
Remember that indexing is an ongoing effort that requires regular monitoring, updates, and adaptation to evolving SEO practices and algorithm changes.
With dedication and strategic implementation of the techniques discussed in this post, you can effectively index your site on Google and pave the way for increased organic traffic and online success.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.
